Nearly all adults have some degree of astigmatism, but most don’t find that it interferes with their lives. However, studies conducted in various countries and cultures show that astigmatism has noticeable effects for approximately one third of adults. Fortunately, contact lenses can be extremely useful in correcting astigmatism — as long as they are carefully selected.
At Stoney Creek Eye Care, we’ve helped countless people find lenses to correct various levels of astigmatism successfully. Read on and discover what kind of lenses might help you see clearly and comfortably again.
What is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a common refractive error that occurs when the cornea or lens in your eye is curved abnormally. This abnormal curve prevents light from focusing properly on the lens after it enters the eye.
Astigmatism can cause various symptoms, such as:
- Distorted or blurry vision at all distances
- Frequent squinting in an attempt to compensate for blurry vision
- Frequent headaches and eye strain from straining muscles while squinting
Adults with astigmatism often experience problems seeing clearly while they drive, while many children with astigmatism find it difficult to focus on blackboards at the front of their classrooms. Since astigmatism poses serious challenges for many vital tasks, correcting it is essential for improving your quality of life.
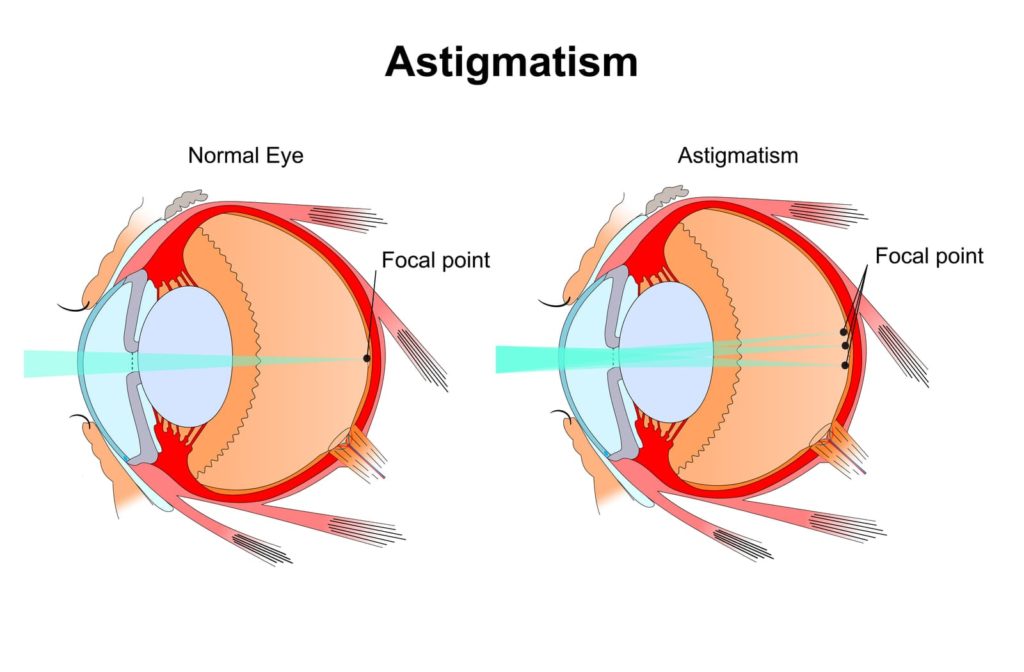
Advantages to Wearing Contacts for Astigmatism
People with astigmatism may have numerous correction options available to them, including glasses, contacts, and laser eye surgery. Contact lenses may be preferable to these other methods because they:
- Provide a wider field of clear vision than glasses
- Are less likely than glasses to be lost or damaged during dynamic activities that require clear vision (such as sports and games)
- Are less expensive than laser eye surgery
- Have fewer associated risks than laser eye surgery (although laser eye surgery is generally considered very safe)
Contact Lens Considerations for People with Astigmatism
Choosing lenses may be more challenging for people with astigmatism than for those with other refractive errors. Not all contacts are designed for people with astigmatism, who often require highly-specialized lenses to focus properly at multiple distances.
If you have astigmatism, it’s vital to visit your eye doctor for a contact lens exam and allow them to recommend lenses that will work for you. During a contact lens exam, your eye doctor will run specific tests to determine what kind of lenses will serve you best.
What Kind of Contacts Work Best for Astigmatism?
Prescriptions with very low astigmatism can often be corrected with soft spherical contact lenses. To achieve this, the contact lense prescription may only need to be slightly modified from the patient’s spectacle prescription. However, patients with moderate or higher amounts of astigmatism need more specialized contact lenses. These include, but are not limited to:
Soft Toric Contact Lenses
Soft contact lenses are generally spherical on both the front and back surface, but toric lenses are designed with a different shape to neutralize astigmatism. The toric shape allows the horizontal and vertical axes of the lens to have different refractive capabilities, which offset refractive errors caused by an oblong cornea.
Lenses must maintain a specific position on the cornea and not rotate in order to maintain clear vision. Soft toric lenses are often weighted on the bottom to prevent movement during blinking and eye movement, allowing them to remain properly positioned.
Pros: soft toric lenses are extremely comfortable, and most people adapt to them easily. They are also available in a wide range of parameters and materials (including breathable silicone hydrogel). Both monthly and daily replacement options are available for soft toric lenses, which lets them accommodate a broad range of lifestyles.
Cons: soft toric lenses are slightly more expensive than spherical soft contact lenses. They may also require a little more time to fit than soft spherical lenses, owing to their more complex shape. Soft toric lenses are also unsuitable for people with very high levels of astigmatism, and must be placed carefully to prevent them from rotating on the cornea and causing vision fluctuations.
Soft toric lenses are best for people with moderate astigmatism who cannot achieve clear vision with soft spherical contact lenses.
Hybrid Contact Lenses
Hybrid lenses add a soft silicone or hydrogel skirt to the basic structure of a rigid lens so that it offers the wearer more comfort. They represent a balance between the comfort of a soft lens and the power of rigid lenses.
Pros: hybrid contact lenses offer the clarity of rigid gas permeable lenses along with the comfort of wearing soft toric lenses.
Cons: hybrid contact lenses are harder and more time-consuming to fit than soft contact lenses (since they must be custom made for each wearer).
Hybrid contact lenses have traditionally been used for patients with mild keratoconus — however, advances in soft contact lens technology have rendered many hybrid contact lenses obsolete, and they are no longer widely used.
Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Contact Lenses
RGP lenses are also known as “hard contact lenses”, and are available in spherical or toric designs. Spherical RGPs can correct moderate levels of astigmatism by neutralizing the refractive error in a patient’s elliptical cornea with their spherical surface. However, high levels of astigmatism require toric RGP designs.
Pros: RGP lenses often confer significant benefits to visual acuity in people with astigmatism, even when it is quite severe. They also do not need to be replaced as frequently as soft toric contact lenses.
Cons: RGP lenses must be custom-made for each patient’s unique prescription and corneal measurements, requiring more initial set-up time than soft lenses. RGP lenses also require more maintenance than other lenses, and may be less comfortable at first because it can take some time for your eyelids to adapt to them.
RGP lenses are best for people who cannot achieve satisfactory vision with soft toric contacts, or whose prescription is not available in a soft toric lens.
Talk to Your Optometrist About the Right Contacts for You
Consulting with a qualified optometrist is the only reliable way to choose contacts that provide both comfort and functionality. If you are considering contact lenses, reach out to us at your earliest convenience and schedule a contact lens exam so that we can help you find appropriate options.